Industrial environments present unique challenges that demand robust measurement solutions capable of withstanding extreme conditions. When precision positioning and accurate displacement measurement are critical, engineers must carefully evaluate whether their chosen instrumentation can perform reliably under harsh operational circumstances. The durability and performance characteristics of measurement devices become paramount considerations in applications ranging from heavy machinery to outdoor installations where environmental factors can significantly impact sensor longevity and accuracy.
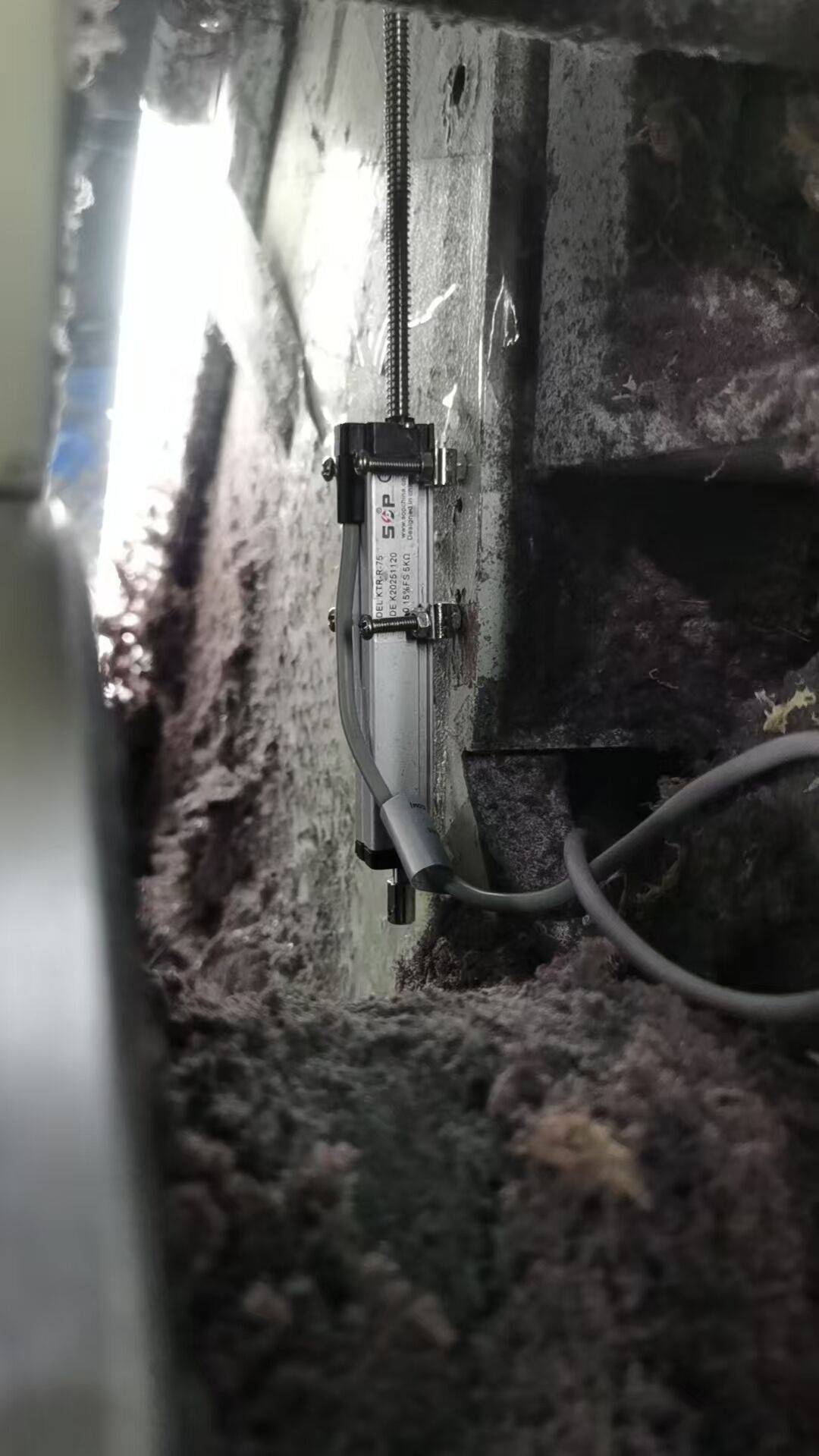

Modern industrial applications frequently expose measurement equipment to conditions that would quickly degrade conventional sensors. Temperature fluctuations, moisture ingress, vibration, shock loads, and corrosive substances create an environment where only specially designed instrumentation can maintain consistent performance over extended periods. Understanding the specific characteristics that enable sensors to operate effectively in these demanding conditions is essential for engineers making critical equipment selection decisions.
Environmental Resistance Characteristics
Temperature Performance Standards
Temperature extremes represent one of the most significant challenges for precision measurement equipment in industrial settings. High-quality sensors designed for harsh environments typically operate across temperature ranges extending from negative forty degrees Celsius to positive eighty degrees Celsius or beyond. This wide operational range ensures consistent performance whether the equipment is deployed in arctic conditions, desert environments, or near high-temperature industrial processes.
The internal components of robust measurement devices must maintain dimensional stability and electrical characteristics across these temperature variations. Advanced materials selection and thermal compensation techniques enable modern sensors to deliver accurate readings regardless of ambient temperature fluctuations. Temperature coefficient specifications indicate how measurement accuracy changes with temperature, with superior devices maintaining minimal drift across their entire operational range.
Thermal cycling resistance becomes particularly important in applications where equipment experiences repeated heating and cooling cycles. The mechanical stress induced by thermal expansion and contraction can lead to component failure in poorly designed sensors, making thermal cycling endurance a critical specification for harsh environment applications.
Moisture and Contamination Protection
Ingress protection ratings provide standardized measurements of how effectively sensors resist moisture and particle contamination. Industrial-grade measurement devices typically achieve IP65 or higher ratings, indicating complete protection against dust ingress and resistance to water jets from any direction. These protection levels ensure reliable operation in washdown environments, outdoor installations, and applications where process fluids may contact the sensor housing.
Sealed construction techniques prevent moisture from reaching sensitive internal components that could cause corrosion, electrical failures, or measurement drift. Advanced sealing methods include welded housings, multiple o-ring barriers, and conformal coating applications on electronic components. These protection measures maintain sensor integrity even when exposed to high-pressure cleaning procedures or submersion conditions.
Chemical resistance becomes equally important in process industries where sensors may encounter corrosive substances. Stainless steel housings, specialized coatings, and chemically inert materials protect measurement devices from aggressive chemicals that would quickly degrade standard instrumentation. Material compatibility charts help engineers select appropriate sensors for specific chemical exposure conditions.
Mechanical Robustness Features
Vibration and Shock Tolerance
Industrial machinery generates significant vibration and occasional shock loads that can damage sensitive measurement equipment. Robust sensors incorporate design features that enable them to withstand continuous vibration exposure while maintaining measurement accuracy. Shock mounting systems, reinforced internal components, and vibration-resistant connection methods protect critical sensor elements from mechanical damage.
Frequency response characteristics determine how sensors perform when subjected to various vibration patterns. Well-designed measurement devices maintain stable output signals across wide frequency ranges, preventing resonance conditions that could amplify vibration effects and compromise accuracy. Damping mechanisms within the sensor structure help isolate sensitive components from external mechanical disturbances.
Shock resistance specifications indicate the maximum acceleration levels sensors can survive without damage or performance degradation. These specifications become particularly important in mobile equipment applications, drop test scenarios, or installations where accidental impacts may occur. Robust construction techniques distribute impact forces throughout the sensor structure, preventing localized stress concentrations that could cause component failures.
Structural Integrity and Mounting Solutions
The mechanical design of measurement sensors must accommodate the mounting constraints and structural requirements of harsh environment installations. Heavy-duty mounting hardware, reinforced connection points, and robust housing designs ensure sensors remain securely positioned despite external forces that might otherwise cause misalignment or mechanical failure.
Material selection plays a crucial role in long-term structural integrity. High-strength aluminum alloys, stainless steel components, and engineered polymers provide the mechanical properties necessary to withstand repeated loading cycles without fatigue failures. Surface treatments and protective coatings enhance corrosion resistance while maintaining mechanical strength characteristics.
Installation flexibility enables sensors to adapt to various mounting configurations without compromising performance. Adjustable mounting brackets, multiple connection options, and standardized interfaces simplify integration into existing equipment while providing the mechanical stability required for accurate measurements. Proper mounting techniques distribute loads effectively and prevent stress concentrations that could affect sensor accuracy over time.
Electrical Performance in Adverse Conditions
Signal Integrity and Noise Immunity
Harsh industrial environments often contain significant electrical noise sources that can interfere with sensitive measurement signals. Advanced sensor designs incorporate shielding techniques, filtering circuits, and differential signal transmission methods to maintain signal integrity despite electromagnetic interference from nearby equipment. These protection measures ensure accurate data transmission even in electrically noisy environments.
Ground loop elimination and proper cable shielding prevent common electrical problems that can cause measurement errors or signal instability. High-quality sensors provide comprehensive grounding instructions and recommend specific cable types to optimize signal transmission performance. Isolation techniques separate measurement circuits from potential interference sources while maintaining accurate signal representation.
Digital signal processing capabilities enable modern sensors to filter noise, compensate for environmental effects, and provide enhanced measurement stability. Advanced algorithms can distinguish between valid measurement signals and environmental interference, automatically adjusting compensation parameters to maintain accuracy across varying operating conditions. These intelligent features reduce the need for external signal conditioning equipment while improving overall system reliability.
Power Supply Considerations
Reliable power delivery becomes critical in harsh environment applications where power supply variations or interruptions could affect measurement accuracy. Robust sensors incorporate wide input voltage ranges, power supply filtering, and voltage regulation circuits to maintain consistent performance despite power quality issues. These features enable operation from various power sources while protecting sensitive internal circuits from electrical transients.
Power consumption optimization extends operational life in battery-powered applications while reducing heat generation that could affect temperature-sensitive components. Low-power design techniques include efficient circuit topologies, sleep mode capabilities, and intelligent power management systems that activate full functionality only when measurements are required.
Surge protection and transient suppression circuits protect sensors from electrical damage caused by lightning, power switching events, or equipment malfunctions. These protection systems automatically divert harmful electrical energy away from sensitive components while maintaining normal operation during typical electrical disturbances. Comprehensive protection schemes address both common-mode and differential-mode interference sources.
Application-Specific Performance Requirements
Accuracy and Resolution Under Stress
Maintaining measurement accuracy under harsh conditions requires sensors to compensate for environmental effects that could introduce errors. Advanced calibration techniques account for temperature effects, mechanical stress, and aging characteristics to provide consistent accuracy throughout the sensor's operational life. Multi-point calibration procedures verify performance across the entire measurement range and environmental operating envelope.
Resolution requirements vary depending on application needs, but harsh environment sensors must maintain their specified resolution despite external disturbances. High-resolution measurement capability enables detection of small position changes while providing the dynamic range necessary for full-scale measurements. Digital signal processing techniques can enhance effective resolution while filtering environmental noise that might otherwise compromise measurement precision.
Long-term stability characteristics ensure that sensor accuracy doesn't degrade significantly over time despite exposure to harsh conditions. Accelerated aging tests and long-term stability studies validate sensor performance over extended operational periods. Quality sensors maintain their calibration accuracy for years of continuous operation without requiring frequent recalibration procedures.
Response Time and Dynamic Performance
Dynamic response characteristics determine how quickly sensors can track rapidly changing positions or detect transient movements. Fast response times enable real-time control applications while adequate bandwidth ensures accurate reproduction of dynamic signals. The linear displacement sensor must balance response speed with noise filtering to provide stable measurements of both static positions and dynamic movements.
Settling time specifications indicate how quickly sensors reach final accuracy after step changes in measured position. Short settling times enable high-speed positioning applications while maintaining measurement accuracy. Overdamped response characteristics prevent oscillations that could cause control system instability while providing adequate speed for most industrial applications.
Frequency response characteristics determine sensor performance when measuring oscillatory or repetitive motions. Flat frequency response across the required bandwidth ensures accurate reproduction of dynamic signals without amplitude or phase distortion. These characteristics become particularly important in vibration monitoring applications or when sensors must track high-frequency position variations.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Field Installation Requirements
Successful deployment of measurement sensors in harsh environments requires careful attention to installation procedures and environmental protection measures. Proper mounting techniques ensure mechanical stability while providing access for maintenance activities. Installation guidelines should address cable routing, environmental sealing, and protection from physical damage during normal operations.
Cable selection and termination methods significantly impact long-term reliability in harsh environment installations. High-quality cables with appropriate insulation, shielding, and jacket materials resist environmental degradation while maintaining signal integrity. Proper termination techniques prevent moisture ingress and maintain electrical connections despite temperature cycling and mechanical stress.
Environmental protection measures extend beyond the sensor itself to include junction boxes, cable conduits, and mounting hardware. Complete system protection ensures reliable operation while simplifying maintenance procedures. Weather-resistant enclosures, drainage provisions, and access covers enable routine maintenance without exposing sensors to environmental hazards.
Preventive Maintenance Strategies
Preventive maintenance programs maximize sensor operational life while minimizing unexpected failures that could disrupt production processes. Regular inspection procedures identify potential problems before they cause measurement errors or sensor failures. Visual inspections check for physical damage, corrosion, or seal degradation that could compromise sensor performance.
Calibration verification procedures confirm that sensors maintain their specified accuracy over time. Periodic calibration checks using certified reference standards detect drift or degradation that might otherwise go unnoticed. Calibration history records track sensor performance trends and help predict when recalibration or replacement might be necessary.
Cleaning procedures remove accumulated contamination that could affect sensor performance or accelerate component degradation. Appropriate cleaning methods and materials prevent damage to sensor surfaces while removing harmful deposits. Regular cleaning schedules based on environmental exposure levels help maintain optimal sensor performance throughout their operational life.
FAQ
What environmental conditions can industrial linear displacement sensors withstand?
Industrial linear displacement sensors designed for harsh environments typically operate across temperature ranges from -40°C to +85°C with IP65 or higher ingress protection ratings. They resist moisture, dust, vibration, shock loads, and chemical exposure depending on their specific construction materials and sealing methods. Advanced models include features like stainless steel housings, welded seals, and conformal coated electronics to withstand extremely harsh conditions including washdown environments and outdoor installations.
How do harsh conditions affect measurement accuracy and what compensations are available?
Environmental factors like temperature variations, mechanical stress, and electromagnetic interference can introduce measurement errors if not properly addressed. Quality sensors incorporate temperature compensation algorithms, thermal coefficient correction, and advanced filtering to maintain accuracy across their operating range. Digital signal processing capabilities automatically adjust for environmental effects while shielding and isolation techniques protect against electrical interference, ensuring consistent accuracy even under adverse conditions.
What maintenance is required for sensors operating in harsh environments?
Preventive maintenance includes regular visual inspections for physical damage or seal degradation, periodic calibration verification using certified standards, and cleaning procedures to remove accumulated contamination. Maintenance frequency depends on environmental severity, but quarterly inspections and annual calibration checks are typical starting points. Proper cable management, environmental sealing verification, and performance trend monitoring help identify potential issues before they cause sensor failures or measurement errors.
How should mounting and installation be approached for maximum durability?
Successful harsh environment installations require rigid mounting systems that resist vibration and shock while providing environmental protection. Use high-quality cables with appropriate shielding and insulation, ensure proper grounding and electrical isolation, and implement comprehensive weather protection for all connection points. Follow manufacturer specifications for mounting torques, cable bend radius, and environmental sealing procedures. Consider accessibility for future maintenance while protecting sensors from physical damage during normal operations.
Table of Contents
- Environmental Resistance Characteristics
- Mechanical Robustness Features
- Electrical Performance in Adverse Conditions
- Application-Specific Performance Requirements
- Installation and Maintenance Considerations
-
FAQ
- What environmental conditions can industrial linear displacement sensors withstand?
- How do harsh conditions affect measurement accuracy and what compensations are available?
- What maintenance is required for sensors operating in harsh environments?
- How should mounting and installation be approached for maximum durability?